R CrB stars
R Coronae Borealis (RCB) are very unusual
type of variable star, in that the variability is caused by the
formation of a cloud of carbon dust in the line of sight. The cloud
is formed near the stellar photosphere, condenses (dimming the star's
visual brightness by several magnitudes) and then dissipates as
it moves away from the star. These star are hydrogen-poor, carbon-
and helium-rich, high-luminosity stars which are simultaneously
eruptive and pulsating variables. All RCB stars are variable at
maximum light because presence of pulsations phenomena, typically
with periods of 40 to 100 days and amplitudes of a few tenths of
a magnitude. They show slow nonperiodic fadings by 1-9 mag in V
lasting from a month or more to several hundred days. The decline
is sharp.
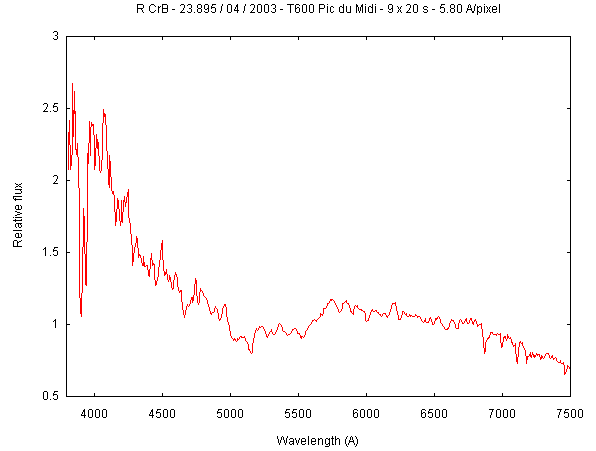
At maximum light the typical spectrum looks like a F or G supergiant but the Balmer lines are very weak or absent. The spectrum is dominated by C2 and CN bands and many lines of neutral atomic carbon.
At the decline period a rich emission-line spectrum appears consisting of singly ionized and neutral metals (CaII H&K, NaI D in the visible part of the spectrum).
R CrB is the prototype of these stars. The number of know R CrB stars is small (26 only in the GCVS). Below a list of brighter members.
HD name R.A. Delta Range Spectral
25878 XX
Cam 04 08 39 +53
21 39 8.1-9.8 G1I(C0-2,0)
247925 SU Tau 05
49 06 +19 04 00 9.1-16.9
G0-1Iep(C1,0 HD)
UW
Cen 12 43 17 -54
31 38 9.1-14.5 K
V854
Cen 14 34 50 -39 33 19 7.1-14.1
Pec
141527 R
CrB 15 48 34 +28
09 25 5.7-14.8 C0,0(F8pep)
RS Tel
18 18 51 -46 34
06 9.0-14.0 C(R0)
GU
Sgr 18 24 16 -24
15 27 11.3 15.0 C(R0)
MV Sgr
18 44 32 -20 57
17 12.0-16.0 B2p(HDCe)
180093 RY Sgr 19
16 33 -33 31 19 5.8-14.0
G0Iaep(C1,0)
U
Aqr 22 03 20 -16
37 40 10.5-14.5 Pec
UV Cas
23 02 15 +59 36
39 11.8-16.5 F0Ib-G5Ib
R CrB