57 Cyg: A spectroscopic binary star
This page describe the observation
of the spectroscopic binary star 59 Cyg.
57 Cyg characteristics:
RA: 20h53.2
DEC: +44°23'
Magnitude: 4.72
Spectral type: B5V+B5V
Period: 2.8548
days
Half amplitude of the radial velocity curve: 111.9 km/s
(primary) and 126.0 km/s (secondary)
Instrumentation:
Flat-field camera 19-cm F/D=4
Audine CCD camera
(CCD KAF-0401E)
R3000 spectrograph (dispersion of 0.93 A/pixel)
Observatory location: Ramonville Saint Agne (near Toulouse, France)
Journal
of observations:
Date
JD
25/07/1999
20H56UT 2451385.370 (your phase 0 point)
01/08/1999 20H08UT 2451392.337
20/08/1999 21H30UT 2451411.396
21/08/1999
19H51UT 2451412.327
22/08/1999 20H15UT
2451413.343
23/08/1999 20H19UT 2451414.347
24/08/1999 20H24UT 2451415.350
29/08/1999 20H52UT 2451420.369
31/08/1999
20H06UT 2451422.337
01/09/1999 20H07UT
2451423.338
02/09/1999 20H28UT 2451424.352
11/09/1999 19H54UT 2451433.329
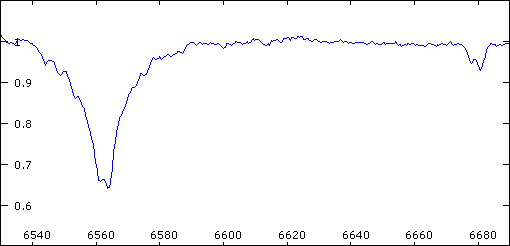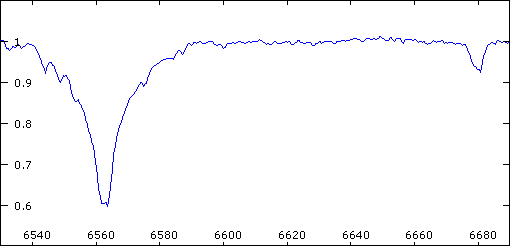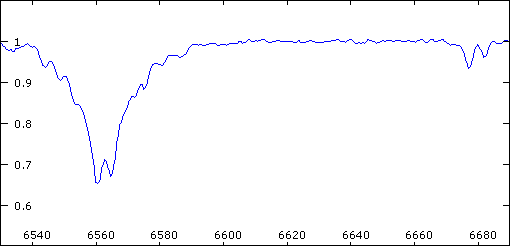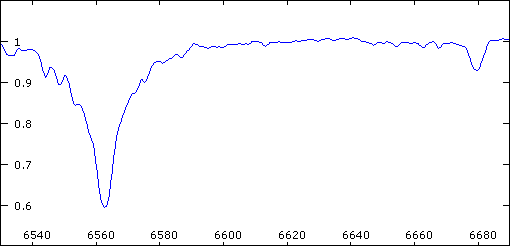
Animation of the 57 Cyg spectrum.
One can see the separation of the H-alpha (6563A) and HeI (6678A)
lines according to the configuration of the orbital couple. The
small lines visibles particularly on the left side of H-alpha correspond
to telluric lines (H2O). The variation of their intensity is caused
by the evolution of the content of moisture of the atmosphere.
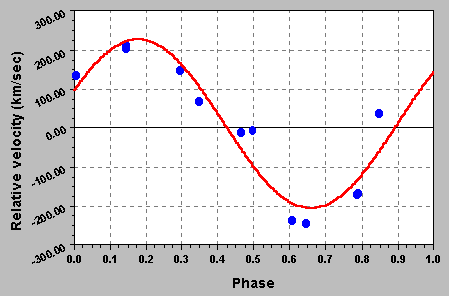
Graphics of the relative radial speed between two
stars in km/s (the whole of the observations made between July 1999
and September 1999 were gathered here). The rotation period adopted
is 2.8548 days. The maximum amplitude radial velocity measured is
about 450 km/s, whereas the value raised in the catalogues is of
2*(111.9*126.0)=475.8 km/s. The agreement is reasonably correct!
A simple sinusoidal curve (in red) is fitted.
Tips:
The phase of a periodical phenomena is given by:
Phase = frac ((JD - JD0) / Period)
where frac() define the fractional part, JD is the Julian Day of the observation, JD0 is an arbitrary starting time (called the Epoch), and Period the period of the phenomena. The following C code show how this is done:
t = (jd - jd0) /
period;
phase = (t - floor(t));
